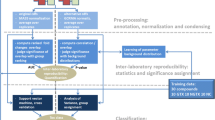
Abstract
Alternative methods to detect non-genotoxic carcinogens are urgently needed, as this class of carcinogens goes undetected in the current testing strategy for carcinogenicity under REACH. A complicating factor is that non-genotoxic carcinogens act through several distinctive modes of action, which makes prediction of their carcinogenic property difficult. We have recently demonstrated that gene expression profiling in primary mouse hepatocytes is a useful approach to categorize non-genotoxic carcinogens according to their modes of action. In the current study, we improved the methods used for analysis and added mouse embryonic stem cells as a second in vitro test system, because of their features complementary to hepatocytes. Our approach involved an unsupervised analysis based on the 30 most significantly up- and down-regulated genes per chemical. Mouse embryonic stem cells and primary mouse hepatocytes were exposed to a selected set of chemicals and subsequently subjected to gene expression profiling. We focused on non-genotoxic carcinogens, but also included genotoxic carcinogens and non-carcinogens to test the robustness of this approach. Application of the optimized comparison approach resulted in improved categorization of non-genotoxic carcinogens. Mouse embryonic stem cells were a useful addition, especially for genotoxic substances, but also for detection of non-genotoxic carcinogens that went undetected by primary hepatocytes. The approach presented here is an important step forward to categorize chemicals, especially those that are carcinogenic.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshari CA, Hamadeh HK, Bushel PR (2011) The evolution of bioinformatics in toxicology: advancing toxicogenomics. Toxicol Sci 120(Suppl 1):S225–S237
Aly HA, Domenech O (2009) Aroclor 1254 induced cytotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction in isolated rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 262(3):175–183
Aragon AD, Quinones GA, Thomas EV, Roy S, Werner-Washburne M (2006) Release of extraction-resistant mRNA in stationary phase Saccharomyces cerevisiae produces a massive increase in transcript abundance in response to stress. Genome Biol 7(2):R9
Attia SM, Kliesch U, Schriever-Schwemmer G, Badary OA, Hamada FM, Adler ID (2003) Etoposide and merbarone are clastogenic and aneugenic in the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test complemented by fluorescence in situ hybridization with the mouse minor satellite DNA probe. Environ Mol Mutagen 41(2):99–103
Bahassi el M (2011) Polo-like kinases and DNA damage checkpoint: beyond the traditional mitotic functions. Exp Biol Med 236(6):648–657
Baranano DE, Rao M, Ferris CD, Snyder SH (2002) Biliverdin reductase: a major physiologic cytoprotectant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(25):16093–16098
Baudoin R, Alberto G, Legendre A et al (2014) Investigation of expression and activity levels of primary rat hepatocyte detoxication genes under various flow rates and cell densities in microfluidic biochips. Biotechnol Prog 30(2):401–410
Beyersmann D, Hartwig A (2008) Carcinogenic metal compounds: recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 82(8):493–512
Criddle DN, Gillies S, Baumgartner-Wilson HK et al (2006) Menadione-induced reactive oxygen species generation via redox cycling promotes apoptosis of murine pancreatic acinar cells. J Biol Chem 281(52):40485–40492
Cui X, Hwang JT, Qiu J, Blades NJ, Churchill GA (2005) Improved statistical tests for differential gene expression by shrinking variance components estimates. Biostatistics 6(1):59–75
Currie RA (2012) Toxicogenomics: the challenges and opportunities to identify biomarkers, signatures and thresholds to support mode-of-action. Mutat Res 746(2):97–103
de Leeuw WC, Rauwerda H, Jonker MJ, Breit TM (2008) Salvaging Affymetrix probes after probe-level re-annotation. BMC Res Notes 1:66
Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, Gmuender H, Bandenburg A, Ahr HJ (2008) Prediction of a carcinogenic potential of rat hepatocarcinogens using toxicogenomics analysis of short-term in vivo studies. MutatRes 637(1–2):23–39
Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, Aubrecht J, Kleinjans JC, Ahr HJ (2009a) Application of toxicogenomics to study mechanisms of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity. Toxicol Lett 186(1):36–44
Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, Fostel JM, Aruga C et al (2009b) Characterization and interlaboratory comparison of a gene expression signature for differentiating genotoxic mechanisms. Toxicol Sci 110(2):341–352
Fidaleo M (2009) Human health risk assessment for peroxisome proliferators: more than 30 years of research. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61(3):215–221
Fielden MR, Adai A, Dunn RT 2nd et al (2011) Development and evaluation of a genomic signature for the prediction and mechanistic assessment of nongenotoxic hepatocarcinogens in the rat. Toxicol Sci 124(1):54–74
Fujiki H, Suganuma M (2009) Carcinogenic aspects of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitors. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 46:221–254
Goetz AK, Singh BP, Battalora M et al (2011) Current and future use of genomics data in toxicology: opportunities and challenges for regulatory applications. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 61(2):141–153
Guyton KZ, Kyle AD, Aubrecht J et al (2009) Improving prediction of chemical carcinogenicity by considering multiple mechanisms and applying toxicogenomic approaches. MutatRes 681(2–3):230–240
Hamawy MM (2003) Molecular actions of calcineurin inhibitors. Drug News Perspect 16(5):277–282
Hand RA, Craven RJ (2003) Hpr6.6 protein mediates cell death from oxidative damage in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 90(3):534–547
Hatakeyama M, Tessier DM, Dunlap DY, Zou E, Matsumura F (2002) Estrogenic action of beta-HCH through activation of c-Neu in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 11(1):27–38
Heise T, Schug M, Storm D et al (2012) In vitro–in vivo correlation of gene expression alterations induced by liver carcinogens. Curr Med Chem 19(11):1721–1730
Hendriks G, Atallah M, Raamsman M et al (2011) Sensitive DsRed fluorescence-based reporter cell systems for genotoxicity and oxidative stress assessment. Mutat Res 709–710:49–59
Hendriks G, Atallah M, Morolli B et al (2012) The ToxTracker assay: novel GFP reporter systems that provide mechanistic insight into the genotoxic properties of chemicals. Toxicol Sci 125(1):285–298
Hernandez LG, van Steeg H, Luijten M, van Benthem J (2009) Mechanisms of non-genotoxic carcinogens and importance of a weight of evidence approach. Mutat Res 682:94–109
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F et al (2003) Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics 4(2):249–264
Jensen SS, Aaberg-Jessen C, Christensen KG, Kristensen B (2013) Expression of the lysosomal-associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP-1) in astrocytomas. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6(7):1294–1305
Keller DA, Juberg DR, Catlin N et al (2012) Identification and characterization of adverse effects in 21st century toxicology. Toxicol Sci 126(2):291–297
Kirkland D, Aardema M, Henderson L, Muller L (2005) Evaluation of the ability of a battery of three in vitro genotoxicity tests to discriminate rodent carcinogens and non-carcinogens I. Sensitivity, specificity and relative predictivity. Mutat Res 584(1–2):1–256
Kirkland D, Aardema M, Muller L, Makoto H (2006) Evaluation of the ability of a battery of three in vitro genotoxicity tests to discriminate rodent carcinogens and non-carcinogens II. Further analysis of mammalian cell results, relative predictivity and tumour profiles. Mutat Res 608(1):29–42
Kitamura M (2010) Induction of the unfolded protein response by calcineurin inhibitors: a double-edged sword in renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transpl Off Publ Eur Dial Transpl Assoc Eur Renal Assoc 25(1):6–9
Kojima H, Sata F, Takeuchi S, Sueyoshi T, Nagai T (2011) Comparative study of human and mouse pregnane X receptor agonistic activity in 200 pesticides using in vitro reporter gene assays. Toxicology 280(3):77–87
Kruse JJ, Svensson JP, Huigsloot M et al (2007) A portrait of cisplatin-induced transcriptional changes in mouse embryonic stem cells reveals a dominant p53-like response. Mutat Res 617(1–2):58–70
Lempiainen H, Muller A, Brasa S et al (2011) Phenobarbital mediates an epigenetic switch at the constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) target gene Cyp2b10 in the liver of B6C3F1 mice. PLoS ONE 6(3):e18216
Lilienblum W, Dekant W, Foth H et al (2008) Alternative methods to safety studies in experimental animals: role in the risk assessment of chemicals under the new European Chemicals Legislation (REACH). Arch Toxicol 82(4):211–236
Magkoufopoulou C, Claessen SM, Tsamou M, Jennen DG, Kleinjans JC, van Delft JH (2012) A transcriptomics-based in vitro assay for predicting chemical genotoxicity in vivo. Carcinogenesis 33(7):1421–1429
Mathijs K, Brauers KJ, Jennen DG et al (2009) Discrimination for genotoxic and nongenotoxic carcinogens by gene expression profiling in primary mouse hepatocytes improves with exposure time. Toxicol Sci 112(2):374–384
Matsuda S, Koyasu S (2000) Mechanisms of action of cyclosporine. Immunopharmacology 47(2–3):119–125
McConnell JL, Wadzinski BE (2009) Targeting protein serine/threonine phosphatases for drug development. Mol Pharmacol 75(6):1249–1261
Melis JP, Derks KW, Pronk TE et al (2014) In vivo murine hepatic microRNA and Mrna expression signatures predicting the (non-)genotoxic carcinogenic potential of chemicals. Arch Toxicol 88(4):1023–1034
Miyamoto S, Yagi H, Yotsumoto F, Kawarabayashi T, Mekada E (2006) Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor as a novel targeting molecule for cancer therapy. Cancer Sci 97(5):341–347
Oh-Hashi K, Koga H, Ikeda S, Shimada K, Hirata Y, Kiuchi K (2010) Role of an ER stress response element in regulating the bidirectional promoter of the mouse CRELD2—ALG12 gene pair. BMC Genom 11:664
Osman AM, van Loveren H (2012) Phosphoproteomic analysis of mouse thymoma cells treated with tributyltin oxide: TBTO affects proliferation and energy sensing pathways. Toxicol Sci 126(1):84–100
Pan C, Gnad F, Olsen JV, Mann M (2008) Quantitative phosphoproteome analysis of a mouse liver cell line reveals specificity of phosphatase inhibitors. Proteomics 8(21):4534–4546
Peters JM, Cheung C, Gonzalez FJ (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and liver cancer: where do we stand? J Mol Med 83(10):774–785
Pfuhler S, Albertini S, Fautz R et al (2007) Genetic toxicity assessment: employing the best science for human safety evaluation part IV: recommendation of a working group of the Gesellschaft fuer Umwelt-Mutationsforschung (GUM) for a simple and straightforward approach to genotoxicity testing. Toxicol Sci 97(2):237–240
Pines A, Kelstrup CD, Vrouwe MG et al (2011) Global phosphoproteome profiling reveals unanticipated networks responsive to cisplatin treatment of embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 31(24):4964–4977
Reubold TF, Eschenburg S (2012) A molecular view on signal transduction by the apoptosome. Cell Signal 24(7):1420–1425
Roos WP, Kaina B (2013) DNA damage-induced cell death: from specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 332(2):237–248
Rubin BS (2011) Bisphenol A: an endocrine disruptor with widespread exposure and multiple effects. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 127(1–2):27–34
Saha BC, Racine FM (2011) Biotechnological production of mannitol and its applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(4):879–891
Saravanabhavan G, Murray J (2012) Human biological monitoring of diisononyl phthalate and diisodecyl phthalate: a review. J Environ Public Health 2012:810501
Sato S, Shirakawa H, Tomita S et al (2008) Low-dose dioxins alter gene expression related to cholesterol biosynthesis, lipogenesis, and glucose metabolism through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathway in mouse liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 229(1):10–19
Schaap MM, Zwart EP, Wackers PF et al (2012) Dissecting modes of action of non-genotoxic carcinogens in primary mouse hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 86:1717–1727
Schug M, Stober R, Heise T et al (2013) Pharmacokinetics explain in vivo/in vitro discrepancies of carcinogen-induced gene expression alterations in rat liver and cultivated hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 87(2):337–345
Silkworth JB, Carlson EA, McCulloch C, Illouz K, Goodwin S, Sutter TR (2008) Toxicogenomic analysis of gender, chemical, and dose effects in livers of TCDD- or aroclor 1254-exposed rats using a multifactor linear model. Toxicol Sci 102(2):291–309
Slob W (2002) Dose-response modeling of continuous endpoints. Toxicol Sci 66(2):298–312
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:Article3
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(16):9440–9445
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545–15550
Tessier DM, Matsumura F (2001) Increased ErbB-2 tyrosine kinase activity, MAPK phosphorylation, and cell proliferation in the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP following treatment by select pesticides. Toxicol Sci 60(1):38–43
Thomas RS, Bao W, Chu TM et al (2009) Use of short-term transcriptional profiles to assess the long-term cancer-related safety of environmental and industrial chemicals. Toxicol Sci 112(2):311–321
Tomasz M (1995) Mitomycin C: small, fast and deadly (but very selective). Chem Biol 2(9):575–579
Tse SY, Mak IT, Weglicki WB, Dickens BF (1990) Chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons promote lipid peroxidation in vascular cells. J Toxicol Environ Health 31(3):217–226
Tsubura A, Lai YC, Miki H et al (2011) Review: animal models of N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary cancer and retinal degeneration with special emphasis on therapeutic trials. In Vivo 25(1):11–22
Tsujimura K, Asamoto M, Suzuki S, Hokaiwado N, Ogawa K, Shirai T (2006) Prediction of carcinogenic potential by a toxicogenomic approach using rat hepatoma cells. Cancer Sci 97(10):1002–1010
van Kesteren PC, Zwart PE, Schaap MM et al (2012) Benzo[a]pyrene-induced transcriptomic responses in primary hepatocytes and in vivo liver: toxicokinetics is essential for in vivo-in vitro comparisons. Arch Toxicol 85:505–515
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ, Bond GL (2008) The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 7(12):979–987
Watanabe T, Suzuki T, Natsume M et al (2012) Discrimination of genotoxic and non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogens by statistical analysis based on gene expression profiling in the mouse liver as determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Mutat Res 747(2):164–175
Waters MD, Jackson M, Lea I (2010) Characterizing and predicting carcinogenicity and mode of action using conventional and toxicogenomics methods. Mutat Res 705(3):184–200
Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A (2003) Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit Rev Toxicol 33(2):105–136
Weng MW, Zheng Y, Jasti VP et al (2010) Repair of mitomycin C mono- and interstrand cross-linked DNA adducts by UvrABC: a new model. Nucleic Acids Res 38(20):6976–6984
Wolfinger RD, Gibson G, Wolfinger ED et al (2001) Assessing gene significance from cDNA microarray expression data via mixed models. J Comput Biol 8(6):625–637
Yamada F, Sumida K, Uehara T et al (2012) Toxicogenomics discrimination of potential hepatocarcinogenicity of non-genotoxic compounds in rat liver. J Appl Toxicol 33(11):1284–1293
Yamauchi S, Kiyosawa N, Ando Y et al (2011) Hepatic transcriptome and proteome responses against diethyl maleate-induced glutathione depletion in the rat. Arch Toxicol 85(9):1045–1056
Acknowledgments
We thank Haziz Jadaar for his contribution to this study. Cyclosporin A was kindly provided by Novartis (Basel, Switzerland). This work was supported by the Netherlands Genomics Initiative/Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research [Grant Number 050-060-510] and the Dutch Technology Foundation STW [Grant Number 06935].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaap, M.M., Wackers, P.F.K., Zwart, E.P. et al. A novel toxicogenomics-based approach to categorize (non-)genotoxic carcinogens. Arch Toxicol 89, 2413–2427 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1368-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1368-6