Abstract
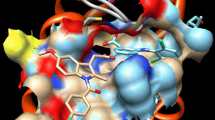
The enzyme phospholipase A2 is responsible for the hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids that release arachidonic acid, which serves as a substrate for pro-inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leucotriens. The binding of the substrate to PLA2 occurs through a well-formed hydrophobic channel. So blocking the hydrophobic channel is an effective way to inhibit PLA2. Compounds inhibiting PLA2 have been implicated as potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of inflammation related diseases. Curcumin is a well studied compound isolated from the plant Curcuma longa. The PLA2 inhibiting activity of curcumin has been studied in our laboratory. The present study focuses whether any of the curcumin analogs can bind PLA2 more strongly than curcumin. To check this, binding of twenty eight different curcumin analogs to PLA2 have been studied by molecular modeling and docking. The mode of interactions of compounds with strong binding are discussed and reported here. It has been observed that four analogs namely rosmarinic acid, tetrahydrocurcumin, dihydrocurucmin and hexahydrocurcumin possess better binding energy than curcumin. The present study may lead to the better understanding of PLA2 inhibition by curcumin analogs. This may help to develop better anti-inflammatory drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg, O.G., Gelb, M.H., Tsai, M.D., Jain, M.K. 2001. Review interfacial enzymology: The secreted phospholipase A2-paradigm. Chem Rev 101, 2613–2654.
Chandra, V., Jasti, J., Kaur, P., Srinivasan, A., Betzel, C., Singh, T.P. 2002. Structural basis of phospholipase A2 inhibition for the synthesis of prostaglandins by the plant alkaloid aristolochic acid from a 1.7 A crystal structure. Biochemistry 41, 10914–10919.
Dijkstra, B.W., Renetseder, R., Kalk, K.H., Hol, W.G., Drenth, J. 1983. Structure of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2 at 2.6 A resolution and comparison with bovine phospholipase A2. J Mol Biol 168, 163–179.
Furnessb, M.S., Robinsonb, T.P., Ehlersb, T., Hubbard, R.B., Arbiserc, J.L., Goldsmithd, D.J., Bowen, J.P. 2005. Antiangiogenic agents: Studies on fumagillin and curcumin analogs. Curr Pharm Des 11, 357–373.
Guo, Z., Su, W., Ma, Z., Smith, G.M., Gong, M.C. 2003. Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 is required for agonist-induced Ca2+ sensitization of contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 278, 1856–1863.
Kohli, K., Ali, J., Ansari, M.J., Raheman, Z. 2005 Curcumin: A natural anti-inflammatory agent. Indian J Pharmacol 37, 141–147.
Liu, Y., Han, X.F., Huang, C.K., Hao, X., Lai, L.H. 2005. Indole-5-phenylcarbamate derivatives as human non-pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15, 4540–4542.
Mukherjee, A.B., Miele, L., Pattabiraman, N. 1994. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Regulation and physiological role. Biochem Pharmacol 48, 1–10.
Mukhopadhyay, A., Basu, N., Ghatak, N., Gujral, P.K. 1982. Anti-inflammatory and irritant activities of curcumin analogues in rats. Agents Actions 12, 508–515.
Nirmal, N., Om Prabha, G., Velmurugan, D. 2008. Modeling studies on phospholipase A2-inhibitor complexes. Indian J Biochem Biophys 45, 256–262.
Singh, R.K., Singh, N., Jabeen, T., Sharma, S., Dey, S., Singh, T.P. 2005. Crystal structure of the complex of group I PLA2 with a group II-specific peptide Leu-Ala-Ile-Tyr-Ser (LAIYS) at 2.6 A resolution. J Drug Target 13, 367–374.
Skrzypczak-Jankun, E., Zhou, K., McCabe, N.P., Selman, S.H., Jankun, J. 2003. Structure of curcumin in complex with lipoxygenase and its significance in cancer. Int J Mol Med 12, 17–24.
Ticli, F.K., Hage, L.I.S., Cambraia, R.S., Pereira, P.S., Magro, A.J., Fontes, M.R.M., Stábeli, J.R., Giglio, R.G., Franc, S.C., Soares, A.M., Sampaio, S.V. 2005. Rosmarinic acid, a new snake venom phospholipases A2 inhibitor from Cordia verbenacea (Boraginceae): Antiserum action potentiation and molecular interaction. Toxicon 46, 318–327.
van den Bergh, C.J., Slotboom, A.J., Verheij, H.M., de Haas, G.H. 1989. The role of Asp-49 and other conserved amino acids in phospholipases A2 and their importance for enzymatic activity. J Cell Biochem 39, 379–390.
Verheij, H.M., Slotboom, A.J., de Haas, G.H. 1981. Structure and function of phospholipase A2. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 91, 91–203.
Verheij, H.M., Volwerk, J.J., Jansen, E.H., Puyk, W.C., Dijkstra, B.W., Drenth, J., de Haas, G.H. 1980. Methylation of histidine-48 in pancreatic phospholipase A2. Role of histidine and calcium ion in the catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry 19, 743–750.
Waite, M. 1987. The Phospholipases. In: Hanahan, D.J. (Ed.) Handbook of Lipid Research. Plenum Press, New York.
Yu, B.Z., Berg, O.G., Jain, M.K. 1993. The divalent cation is obligatory for the binding of ligands to the catalytic site of secreted phospholipase A2. Biochemistry 32, 6485–6492.
Yuan, C., Byeon, I.J., Poi, M.J., Tsai M.D. 1999. Structural analysis of phospholipase A2 from functional perspective. II. Characterization of a molten globule-like state induced by site-specific mutagenesis. Biochemistry 38, 2919–2929.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dileep, K.V., Tintu, I. & Sadasivan, C. Molecular docking studies of curcumin analogs with phospholipase A2. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 3, 189–197 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-011-0090-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-011-0090-9