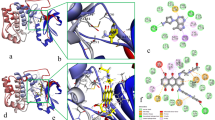
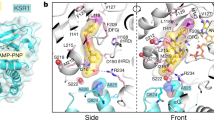
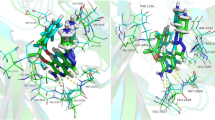
Abstract
Trametinib was endorsed by the FDA in 2013 as a single agent for adult melanoma patients. Trametinib inhibits cell growth and proliferation in multiple tumor xenografts by preventing RAF phosphorylation of MEK and thus restricting accumulation of activated MEK. In this study, the focus of investigation was the mechanism of the interaction between trametinib and MEK1/2 via computational simulation. To specify the best interaction site of inhibitor with MEK1/2 based on the interaction energy ranking, first we performed a docking and then we studied the interactions of the ATP-bound MEK with trametinib, with RAF and the complex of the ATP-bound MEK–trametinib with RAF via molecular dynamic simulations. The results showed that trametinib inactivates the enzyme by bonding to a group of amino acids including Lys97/101, SER218/216, Asp208/212, and Met143/147 in MEK1/2. By bonding to the essential amino acids, trametinib inhibits the activity of the enzyme. All in all, the acquired results can be of great use in designing new inhibitors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohren JF, Chen H, Pavlovsky A, Whitehead C, Zhang E, Kuffa P, Yan C, McConnell P, Spessard C, Banotai C, Mueller WT, Delaney A, Omer C, Sebolt-Leopold J, Dudley DT, Leung IK, Flamme C, Warmus J, Kaufman M, Barrett S, Tecle H, Hasemann C a (2004) Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(12):1192–1197. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb859
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W (2007) MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 26(22):3279–3290. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210421
Kim EK, Choi E-J (2010) Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. Elsevier BV 1802(4):396–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.12.009
Miller CR, Oliver KE, Farley JH (2014) MEK1/2 inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic malignancies. Gynecol Oncol Elsevier Inc. 133(1):128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.01.008
Peyssonnaux C, Eychène A (2001) The Raf/MEK/ERK pathway: new concepts of activation. Biol Cell 93:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0248-4900(01)01125-X
Wright CJM, McCormack PL (2013) Trametinib: first global approval. Drugs 73(11):1245–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-013-0096-1
Yamaguchi T, Kakefuda R, Tajima N, Sowa Y, Sakai T (2011) Antitumor activities of JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), a novel MEK1/2 inhibitor, on colorectal cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Int J Oncol 39(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2011.1015
Robarge KD, Lee W, Eigenbrot C, Ultsch M, Wiesmann C, Heald R, Price S, Hewitt J, Jackson P, Savy P, Burton B, Choo EF, Pang J, Boggs J, Yang A, Yang X, Baumgardner M (2014) Structure based design of novel 6,5 heterobicyclic mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors leading to the discovery of imidazo[1,5-a] pyrazine G-479. Bioorg Med Chem Lett Elsevier Ltd 24(19):4714–4723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.08.008
Gilmartin AG, Bleam MR, Groy A, Moss KG, Minthorn EA, Kulkarni SG, Rominger CM, Erskine S, Fisher KE, Yang J, Zappacosta F, Annan R, Sutton D, Laquerre SG (2011) GSK1120212 (JTP-74057) is an inhibitor of MEK activity and activation with favorable pharmacokinetic properties for sustained in vivo pathway inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 17(5):989–1000. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2200
Ramezani F, Amanlou M, Rafii-Tabar H (2014) Gold nanoparticle shape effects on human serum albumin corona interface: a molecular dynamic study. J Nanopart Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-014-2512-1
Ramezani F, Amanlou M, Rafii-Tabar H (2014) Comparison of amino acids interaction with gold nanoparticle. Amino Acids 46(4):911–920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1642-6
Ramezani F, Rafii-Tabar H (2015) ‘An in-depth view of human serum albumin corona on gold nanoparticles. Mol BioSyst R Soc Chem 11(2):454–462. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MB00591K
Hartung IV, Hitchcock M, Pühler F, Neuhaus R, Scholz A, Hammer S, Petersen K, Siemeister G, Brittain D, Hillig RC (2013) Optimization of allosteric MEK inhibitors. Part 1: venturing into underexplored SAR territories. Bioorg Med Chem Lett Elsevier Ltd 23(8):2384–2390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.028
Haling JR, Sudhamsu J, Yen I, Sideris S, Sandoval W, Phung W, Bravo BJ, Giannetti AM, Peck A, Masselot A, Morales T, Smith D, Brandhuber BJ, Hymowitz SG, Malek S (2014) Structure of the BRAF-MEK complex reveals a kinase activity independent role for BRAF in MAPK signaling. Cancer Cell Elsevier Inc 26(3):402–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.007
Nancy M (2006) ChemDraw Ultra 10.0 CambridgeSoft, 100 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140. www.cambridgesoft.com. Commercial Price: $1910 for download, $2150 for CD-ROM; Academic Price: $710 for download, $800 for CD-ROM. J Am Chem Soc 128(41):13649–13650. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0697875
Lito P, Saborowski A, Yue J, Solomon M, Joseph E, Gadal S, Saborowski M, Kastenhuber E, Fellmann C, Ohara K, Morikami K, Miura T, Lukacs C, Ishii N, Lowe S, Rosen N (2014) Article disruption of CRAF-mediated MEK activation is required for effective MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant tumors. Cancer Cell Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.011
Rebecca VW, Smalley KSM (2015) Change or die: targeting adaptive signaling to kinase inhibition in cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol Elsevier Inc 91(4):417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.07.031
Naidoo A, Naidoo K, Yende-zuma N, Gengiah TN (2015) NIH Public Access 19(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.3851/IMP2701.Changes
Peng YH, Shiao HY, Tu CH, Liu PM, Hsu JTA, Amancha PK, Wu JS, Coumar MS, Chen CH, Wang SY, Lin WH, Sun HY, Chao YS, Lyu PC, Hsieh HP, Wu SY (2013) Protein kinase inhibitor design by targeting the Asp-Phe-Gly (DFG) motif: the role of the DFG motif in the design of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Med Chem 56(10):3889–3903. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm400072p
Roskoski R (2012) MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun Elsevier Inc 417(1):5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.11.145
Yari H, Ganjalikhany MR, Sadegh HR (2015) In silico investigation of new binding pocket for mitogen activated kinase kinase (MEK): development of new promising inhibitors. Comput Biol Chem 59:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2015.09.013
Fischmann TO, Smith CK, Mayhood TW, Jr EM, Reichert P, Mannarino A, Carr D, Zhu H, Wong J, Yang R, Le HV, Madison VS, Myers JE (2009) ‘Crystal structures of MEK1 binary and ternary complexes with nucleotides and inhibitors crystal structures of MEK1 binary and ternary complexes with nucleotides and inhibitors. Society. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi801898e
Hong DS, Vence L, Falchook G, Radvanyi LG, Liu C, Goodman V, Legos JJ, Blackman S, Scarmadio A, Kurzrock R, Lizee G, Hwu P (2012) ‘BRAF(V600) inhibitor GSK2118436 targeted inhibition of mutant BRAF in cancer patients does not impair overall immune competency’. Clin Cancer Res 18(8):2326–2335. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2515
Acknowledgements
This study is related to the project NO. 1397/44135 From Student Research Committee, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. We also appreciate the “Student Research Committee” and “Research & Technology Chancellor” in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for their financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemzadeh, S., Ramezani, F. & Rafii-Tabar, H. Study of Molecular Mechanism of the Interaction Between MEK1/2 and Trametinib with Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 11, 115–124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-018-0305-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-018-0305-4