Abstract
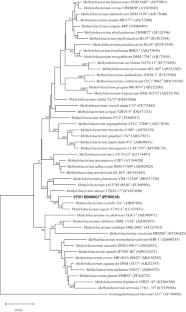
An aerobic, Gram-stain-negative, motile rod bacterium, designated as SYSU BS000021T, was isolated from a black soil sample in Harbin, Heilongjiang province, China. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that the isolate belongs to the genus Methylobacterium, and showed the highest sequence similarity to Methylobacterium segetis KCTC 62267 T (98.51%) and Methylobacterium oxalidis DSM 24028 T (97.79%). Growth occurred at 20–37℃ (optimum, 28 °C), pH 6.0–8.0 (optimum, pH 7.0) and in the presence of 0% (w/v) NaCl. Polar lipids comprised of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, one unidentified aminolipid and one unidentified polar lipid. The major cellular fatty acids (> 5%) were C18:0 and C18:1 ω7c and/or C18:1 ω6c. The predominant respiratory quinone was Q-10. The genomic G + C content was 68.36% based on the whole genome analysis. The average nucleotide identity (≤ 83.5%) and digital DNA–DNA hybridization (≤ 27.3%) values between strain SYSU BS000021T and other members of the genus Methylobacterium were all lower than the threshold values recommended for distinguishing novel prokaryotic species. Based on the results of phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic analyses, strain SYSU BS000021T represents a novel species of the genus Methylobacterium, for which the name Methylobacterium nigriterrae sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of the proposed novel species is SYSU BS000021T (= GDMCC 1.3814 T = KCTC 8051 T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain SYSU BS000021T has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number PP380194. Whole Genome Shotgun project of strain SYSU BS000021T has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under accession number JBAWTG000000000. The genome raw data of strain SYSU BS000021T has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number SRR28216103. Four supplementary tables and four supplementary figures are included on the online supplementary file.
Abbreviations
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA–DNA hybridization
- ML:
-
Maximum-likelihood
- MP:
-
Maximum-parsimony
- NJ:
-
Neighbour-joining
- R2A:
-
Reasoner’s 2A
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
- PG:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol
- DPG:
-
Diphosphatidylglycerol
- AL:
-
Aminolipid
- L:
-
Polar lipid
References
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Blin K, Shaw S, Kloosterman AM et al (2021) antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W29–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab335
Bok JD, Yernool DA, Eveleigh DE (1998) Purification, characterization, and molecular analysis of thermostable cellulases CelA and CelB from Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4774–4781. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.64.12.4774-4781.1998
Boutet E, Lieberherr D, Tognolli M et al. (2016) UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: how to use the entry view. Plant bioinformatics: methods and protocols, 23–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3167-5_2
Buck JD (1982) Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of Gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.44.4.992-993.1982
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C et al (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D233–D238. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn663
Caspi R, Billington R, Fulcher CA et al (2018) The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D633–D639. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx935
Chaumeil PA, Mussig AJ, Hugenholtz P et al (2020) GTDB-Tk: a toolkit to classify genomes with the Genome Taxonomy Database. Bioinformatics 36:1925–1927. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz848
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y et al (2018) fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34:i884–i890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chistoserdova L (2011) Modularity of methylotrophy, revisited. Environ Microbiol 13:2603–2622. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02464.x
Choi O, Kim J, Kim JG et al (2008) Pyrroloquinoline quinone is a plant growth promotion factor produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens B16. Plant Physiol 146:657. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.112748
Collins MD, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE et al (1985) Menaquinone composition of mycolic acid-containing actinomycetes and some sporoactinomycetes. J Appl Bacteriol 58:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01431.x
Da Mota FF, Gomes EA, Paiva E et al (2004) Use of rpoB gene analysis for identification of nitrogen-fixing Paenibacillus species as an alternative to the 16S rRNA gene. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2004.01536.x
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Feng XM, Mo YX, Han L et al (2015) Qipengyuania sediminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Erythrobacteraceae isolated from subterrestrial sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3658–3665. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000472
Feng GD, Chen W, Zhang XJ et al (2020) Methylobacterium nonmethylotrophicum sp. nov., isolated from tungsten mine tailing. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2867–2872. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004112
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Biol 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Gallego V, García MT, Ventosa A (2005) Methylobacterium hispanicum sp. nov. and Methylobacterium aquaticum sp. nov., isolated from drinking water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63319-0
Galperin MY, Makarova KS, Wolf YI et al (2015) Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D261–D269. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1223
Gonzalez C, Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. An amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715. https://doi.org/10.1139/m78-119
Green PN, Ardley JK (2018) Review of the genus Methylobacterium and closely related organisms: a proposal that some Methylobacterium species be reclassified into a new genus, Methylorubrum gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:2727–2748. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002856
Green PN, Bousfield IJ (1982) A taxonomic study of some Gram-negative facultatively methylotrophic bacteria. Microbiology 128:623–638. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-128-3-623
Grossi CEM, Fantino E, Serral F et al (2020) Methylobacterium sp. 2A is a plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that has the potential to improve potato crop yield under adverse conditions. Front Plant Sci 11:71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00071
Jia B, Raphenya AR, Alcock B et al (2017) CARD 2017: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D566–D573. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1004
Jiao JY, Fu L, Hua ZS et al (2021a) Insight into the function and evolution of the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway in Actinobacteria. ISME J 15:3005–3018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-00935-9
Jiao JY, Liu L, Hua ZS et al (2021b) Microbial dark matter coming to light: challenges and opportunities. Natl Sci Rev 8:nwaa280. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa280
Jiao JY, Lian ZH, Li MM et al (2022) Comparative genomic analysis of Thermus provides insights into the evolutionary history of an incomplete denitrification pathway. mLife 1:198–209. https://doi.org/10.1002/mlf2.12009
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M et al (2017) KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D353–D361. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1092
Kato Y, Asahara M, Goto K et al (2008) Methylobacterium persicinum sp. nov., Methylobacterium komagatae sp. nov., Methylobacterium brachiatum sp. nov., Methylobacterium tardum sp. nov. and Methylobacterium gregans sp. nov., isolated from freshwater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1134–1141. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65583-0
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chromatogr 5:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1080/01483918208067640
Kumar M, Tomar RS, Lade H et al (2016) Methylotrophic bacteria in sustainable agriculture. World J Microb Biot 32:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2074-8
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M et al (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Letunic I, Bork P (2021) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W293–W296. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab301
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P et al (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China), and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64749-0
Liu B, Zheng D, Jin Q et al (2019) VFDB 2019: a comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D687–D692. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1080
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S (2014) Methylobacterium pseudosasicola sp. nov. and Methylobacterium phyllostachyos sp. nov., isolated from bamboo leaf surfaces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2376–2384. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.057232-0
Madhaiyan M, Suresh Reddy BV, Anandham R et al (2006) Plant growth–promoting Methylobacterium induces defense responses in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) compared with rot pathogens. Curr Microbiol 53:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0452-9
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP et al (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01172.x
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, Von Haeseler A et al (2015) IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 32:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msu300
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT et al. (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res, 25:1043–1055. http://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.186072.114
Patt TE, Cole GC, Hanson RS (1976) Methylobacterium, a new genus of facultatively methylotrophic bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 26:226–229. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-26-2-226
Pritchard L, Glover RH, Humphris S et al (2016) Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal Methods 8:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY02550H
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sayers EW, Agarwala R, Bolton EE et al (2019) Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D23. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1069
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Shi W, Sun Q, Fan G et al (2021) gcType: a high-quality type strain genome database for microbial phylogenetic and functional research. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D694–D705. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa957
Tamaoka J, Katayama-Fujimura Y, Kuraishi H (1983) Analysis of bacterial menaquinone mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Bacteriol 54:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01297.x
Tambalo DD, Del Bel KL, Bustard DE et al (2010) Regulation of flagellar, motility and chemotaxis genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum by the VisN/R-Rem cascade. Microbiology 156:1673–1685. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.035386-0
Tani A, Sahin N, Kimbara K (2012) Methylobacterium oxalidis sp. nov., isolated from leaves of Oxalis corniculata. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1647–1652. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.033019-0
Ten LN, Li W, Elderiny NS et al (2020) Methylobacterium segetis sp. nov., a novel member of the family Methylobacteriaceae isolated from soil on Jeju Island. Arch Microbiol 202:747–754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01784-z
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F et al (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Urban M, Cuzick A, Rutherford K et al (2017) PHI-base: a new interface and further additions for the multi-species pathogen–host interactions database. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D604–D610. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1089
Veyisoglu A, Camas M, Tatar D et al (2013) Methylobacterium tarhaniae sp. nov., isolated from arid soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2823–2828. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.049551-0
Wang X, Sahr F, Xue T et al (2007) Methylobacterium salsuginis sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1699–1703. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64877-0
Xu P, Li WJ, Tang SK et al (2005) Naxibacter alkalitolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family ‘Oxalobacteraceae’ isolated from China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1149–1153. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63407-0
Yang ZW, Lian ZH, Liu L et al (2023) Cultivation strategies for prokaryotes from extreme environments. iMeta 2:e123. https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.123
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. Aharon Oren (The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel) for helping with the etymology.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFD1500300) and the National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2021FY100900). WJL and SW were also supported by Introduction project of high-level talents in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WJL, SW, JYJ designed the research and project outline. YTOY isolated the bacterium. LL and TTS performed the genomic data analysis. LBC, YW, JYX, PJJ, RRH, and WYP performed the deposition, physiological and chemotaxonomic experiments. LBC drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, LB., OuYang, YT., Liu, L. et al. Methylobacterium nigriterrae sp. nov., isolated from black soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 117, 83 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-024-01981-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-024-01981-x




