Summary
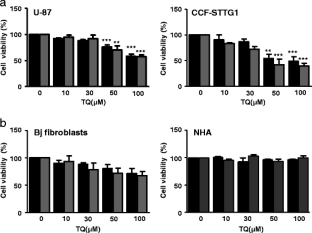
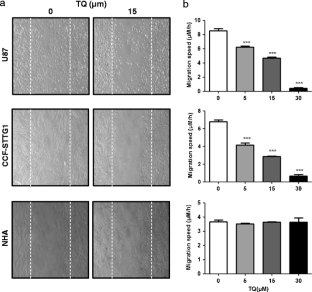
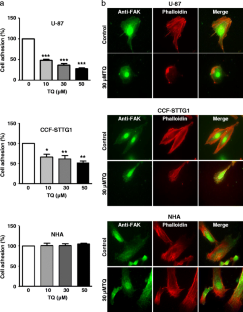
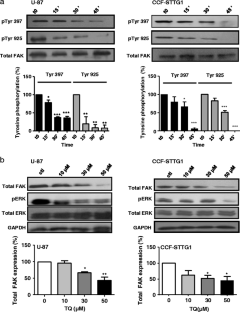
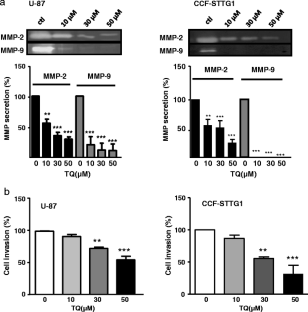
Glioblastoma represent the most frequent primary tumors of the central nervous system and remain among the most aggressive human cancers as available therapeutic approaches still fail to contain their invasiveness. Many studies have reported elevated expression of the Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) protein in glioblastoma, associated with an increase in the rates of both migration and invasion. This designates FAK as a promising target to limit invasiveness in glioblastoma. Thymoquinone (TQ), the main phytoactive compound of Nigella sativa has shown remarkable anti-neoplasic activities on a variety of cancer cells. Here, we studied the anti-invasive and anti-migratory effects of TQ on human glioblastoma cells. The results obtained indicated that TQ treatment reduced migration, adhesion and invasion of both U-87 and CCF-STTG1 cells. This was accompanied by a drastic down-regulation of FAK, associated with a reduction of ERK phosphorylation as well as MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion. This study provides new data on FAK regulation by a natural product (TQ) which could be of a great value for the development of novel therapies in glioblastoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mangiola A, Anile C, Pompucci A, Capone G, Rigante L, De Bonis P (2010) Glioblastoma therapy: going beyond Hercules Columns. Expert Rev Neurother 10(4):507–514
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60(3):166–193
Zhao J, Guan JL (2009) Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):35–49
Schlaepfer DD, Mitra SK, Ilic D (2004) Control of motile and invasive cell phenotypes by focal adhesion kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1692(2–3):77–102
Lark AL, Livasy CA, Dressler L, Moore DT, Millikan RC, Geradts J, Iacocca M, Cowan D, Little D, Craven RJ, Cance W (2005) High focal adhesion kinase expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with an aggressive phenotype. Mod Pathol 18(10):1289–1294
Lark AL, Livasy CA, Calvo B, Caskey L, Moore DT, Yang X, Cance WG (2003) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in primary colorectal carcinomas and colorectal liver metastases: immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Cancer Res 9(1):215–222
Beierle EA, Massoll NA, Hartwich J, Kurenova EV, Golubovskaya VM, Cance WG, McGrady P, London WB (2008) Focal adhesion kinase expression in human neuroblastoma: immunohistochemical and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Cancer Res 14(11):3299–3305
Natarajan M, Hecker TP, Gladson CL (2003) FAK signaling in anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma tumors. Cancer journal (Sudbury, Mass 9 (2):126–133
Hecker TP, Grammer JR, Gillespie GY, Stewart J Jr, Gladson CL (2002) Focal adhesion kinase enhances signaling through the Shc/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in anaplastic astrocytoma tumor biopsy samples. Cancer Res 62(9):2699–2707
Jones G, Machado J Jr, Tolnay M, Merlo A (2001) PTEN-independent induction of caspase-mediated cell death and reduced invasion by the focal adhesion targeting domain (FAT) in human astrocytic brain tumors which highly express focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Cancer Res 61(15):5688–5691
Treasure J (2005) Herbal medicine and cancer: an introductory overview. Semin Oncol Nurs 21(3):177–183
Gali-Muhtasib H, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R (2006) Thymoquinone: a promising anti-cancer drug from natural sources. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38(8):1249–1253
Padhye S, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Mohammad R, Sarkar FH (2008) From here to eternity - the secret of Pharaohs: Therapeutic potential of black cumin seeds and beyond. Canc Ther 6(b):495–510
Banerjee S, Padhye S, Azmi A, Wang Z, Philip PA, Kucuk O, Sarkar FH, Mohammad RM (2010) Review on molecular and therapeutic potential of thymoquinone in cancer. Nutr Cancer 62(7):938–946
Al-Ali A, Alkhawajah AA, Randhawa MA, Shaikh NA (2008) Oral and intraperitoneal LD50 of thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa, in mice and rats. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 20(2):25–27
Gali-Muhtasib H, Ocker M, Kuester D, Krueger S, El-Hajj Z, Diestel A, Evert M, El-Najjar N, Peters B, Jurjus A, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R (2008) Thymoquinone reduces mouse colon tumor cell invasion and inhibits tumor growth in murine colon cancer models. J Cell Mol Med 12(1):330–342
Jafri SH, Glass J, Shi R, Zhang S, Prince M, Kleiner-Hancock H (2010) Thymoquinone and cisplatin as a therapeutic combination in lung cancer: In vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:87
Yi T, Cho SG, Yi Z, Pang X, Rodriguez M, Wang Y, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2008) Thymoquinone inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol Cancer Ther 7(7):1789–1796
Ivankovic S, Stojkovic R, Jukic M, Milos M, Milos M, Jurin M (2006) The antitumor activity of thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone in vitro and in vivo. Exp Oncol 28(3):220–224
El-Najjar N, Chatila M, Moukadem H, Vuorela H, Ocker M, Gandesiri M, Schneider-Stock R, Gali-Muhtasib H (2010) Reactive oxygen species mediate thymoquinone-induced apoptosis and activate ERK and JNK signaling. Apoptosis 15(2):183–195
Gurung RL, Lim SN, Khaw AK, Soon JF, Shenoy K, Mohamed Ali S, Jayapal M, Sethu S, Baskar R, Hande MP (2010) Thymoquinone induces telomere shortening, DNA damage and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One 5(8):e12124
Rondé P, Giannone G, Gerashymova I, Stoeckel H, Takeda K, Haiech J (2000) Mechanism of calcium oscillations in migrating human astrocytoma cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (Molecular Cell Research) 1498:273–280
Cecarini V, Quassinti L, Di Blasio A, Bonfili L, Bramucci M, Lupidi G, Cuccioloni M, Mozzicafreddo M, Angeletti M, Eleuteri AM (2010) Effects of thymoquinone on isolated and cellular proteasomes. FEBS J 277(9):2128–2141
Xu HY, Qian AR, Shang P, Xu J, Kong LM, Bian HJ, Chen ZN (2007) siRNA targeted against HAb18G/CD147 inhibits MMP-2 secretion, actin and FAK expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line via ERK1/2 pathway. Cancer Lett 247(2):336–344
Mon NN, Hasegawa H, Thant AA, Huang P, Tanimura Y, Senga T, Hamaguchi M (2006) A role for focal adhesion kinase signaling in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9 production in a cholangiocarcinoma cell line, CCKS1. Cancer Res 66(13):6778–6784
Mon NN, Ito S, Senga T, Hamaguchi M (2006) FAK signaling in neoplastic disorders: a linkage between inflammation and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1086:199–212
Shoieb AM, Elgayyar M, Dudrick PS, Bell JL, Tithof PK (2003) In vitro inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in cancer cell lines by thymoquinone. Int J Oncol 22(1):107–113
Gali-Muhtasib H, Diab-Assaf M, Boltze C, Al-Hmaira J, Hartig R, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R (2004) Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent mechanism. Int J Oncol 25(4):857–866
El-Mahdy MA, Zhu Q, Wang QE, Wani G, Wani AA (2005) Thymoquinone induces apoptosis through activation of caspase-8 and mitochondrial events in p53-null myeloblastic leukemia HL-60 cells. Int J Cancer 117(3):409–417
Abusnina A, Alhosin M, Keravis T, Muller CD, Fuhrmann G, Bronner C, Lugnier C (2011) Down-regulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE1A is the key event of p73 and UHRF1 deregulation in thymoquinone-induced acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell apoptosis. Cell Signal 23(1):152–160
Webb DJ, Donais K, Whitmore LA, Thomas SM, Turner CE, Parsons JT, Horwitz AF (2004) FAK-Src signalling through paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly. Nat Cell Biol 6(2):154–161
Schaller MD (2010) Cellular functions of FAK kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 7):1007–1013
Parsons JT (2003) Focal adhesion kinase: the first 10 years. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 8):1409–1416
Grisaru-Granovsky S, Salah Z, Maoz M, Pruss D, Beller U, Bar-Shavit R (2005) Differential expression of protease activated receptor 1 (Par1) and pY397FAK in benign and malignant human ovarian tissue samples. Int J Cancer 113(3):372–378
Aronsohn MS, Brown HM, Hauptman G, Kornberg LJ (2003) Expression of focal adhesion kinase and phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Laryngoscope 113(11):1944–1948
Hamadi A, Bouali M, Dontenwill M, Stoeckel H, Takeda K, Ronde P (2005) Regulation of focal adhesion dynamics and disassembly by phosphorylation of FAK at tyrosine 397. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 19):4415–4425
Brunton VG, Avizienyte E, Fincham VJ, Serrels B, Metcalf CA 3rd, Sawyer TK, Frame MC (2005) Identification of Src-specific phosphorylation site on focal adhesion kinase: dissection of the role of Src SH2 and catalytic functions and their consequences for tumor cell behavior. Cancer Res 65(4):1335–1342
Deramaudt TB, Dujardin D, Hamadi A, Noulet F, Kolli K, De Mey J, Takeda K, Ronde P (2011) FAK phosphorylation at Tyr-925 regulates cross-talk between focal adhesion turnover and cell protrusion. Mol Biol Cell 22(7):964–975
Kaneda T, Sonoda Y, Ando K, Suzuki T, Sasaki Y, Oshio T, Tago M, Kasahara T (2008) Mutation of Y925F in focal adhesion kinase (FAK) suppresses melanoma cell proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett 270(2):354–361
Torres MP, Ponnusamy MP, Chakraborty S, Smith LM, Das S, Arafat HA, Batra SK (2010) Effects of thymoquinone in the expression of mucin 4 in pancreatic cancer cells: implications for the development of novel cancer therapies. Mol Cancer Ther 9(5):1419–1431
Yi T, Cho SG, Yi Z, Luo W, Wang Y, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2008) Thymoquinone inhibits angiogenesis and prostate tumor growth by suppressing MAPK signaling pathways. The FASEB Journal 22:654.1
Koka PS, Mondal D, Schultz M, Abdel-Mageed AB, Agrawal KC (2010) Studies on molecular mechanisms of growth inhibitory effects of thymoquinone against prostate cancer cells: role of reactive oxygen species. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood) 235(6):751–760
Chen HC, Appeddu PA, Isoda H, Guan JL (1996) Phosphorylation of tyrosine 397 in focal adhesion kinase is required for binding phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 271(42):26329–34
Golubovskaya VM, Finch R, Cance WG (2005) Direct interaction of the N-terminal domain of focal adhesion kinase with the N-terminal transactivation domain of p53. J Biol Chem 280(26):25008–21
Singh G, Chan AM (2001) Post-translational modifications of PTEN and their potential therapeutic implications. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11(5):536–47
Gu J, Tamura M, Pankov R, Danen EH, Takino T, Matsumoto K, Yamada KM (1999) Shc and FAK differentially regulate cell motility and directionality modulated by PTEN. J Cell Biol 146:389–403
Giannone G, Rondé P, Gaire M, Haiech J, Takeda K (2002) Calcium oscillations trigger focal adhesion disassembly in human U87 astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem 277:26364–26371
Hu B, Jarzynka MJ, Guo P, Imanishi Y, Schlaepfer DD, Cheng SY (2006) Angiopoietin 2 induces glioma cell invasion by stimulating matrix metalloprotease 2 expression through the alphavbeta1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res 66(2):775–783
Lu W, Zhou X, Hong B, Liu J, Yue Z (2004) Suppression of invasion in human U87 glioma cells by adenovirus-mediated co-transfer of TIMP-2 and PTEN gene. Cancer Lett 214(2):205–213
Yip D, Ahmad A, Karapetis CS, Hawkins CA, Harper PG (1999) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors: applications in oncology. Invest New Drugs 17(4):387–399
Uhm JH, Dooley NP, Villemure JG, Yong VW (1997) Mechanisms of glioma invasion: role of matrix-metalloproteinases. Can J Neurol Sci 24(1):3–15
Park JB, Kwak HJ, Lee SH (2008) Role of hyaluronan in glioma invasion. Cell Adh Migr 2(3):202–207
Schlaepfer DD, Hanks SK, Hunter T, van der Geer P (1994) Integrin-mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by GRB2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 372(6508):786–791
Schlaepfer DD, Hunter T (1997) Focal adhesion kinase overexpression enhances ras-dependent integrin signaling to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase through interactions with and activation of c-Src. J Biol Chem 272(20):13189–13195
Schlaepfer DD, Jones KC, Hunter T (1998) Multiple Grb2-mediated integrin-stimulated signaling pathways to ERK2/mitogen-activated protein kinase: summation of both c-Src- and focal adhesion kinase-initiated tyrosine phosphorylation events. Mol Cell Biol 18(5):2571–2585
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Ligue Contre le Cancer (Comités de la région Alsace) to P. Rondé. K. Kolli-Bouhafs was supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Ministère de l’Enseignement et de la Recherche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolli-Bouhafs, K., Boukhari, A., Abusnina, A. et al. Thymoquinone reduces migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells associated with FAK, MMP-2 and MMP-9 down-regulation. Invest New Drugs 30, 2121–2131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9777-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-011-9777-3