Open AccessArticle
A New CPX Drum Test to Obtain Sound Pressure Levels of Tyre Noise for Type Approval
by
David Clar-Garcia, Hector Campello-Vicente, Nuria Campillo-Davo, Miguel Sanchez-Lozano and Emilio Velasco-Sanchez
Acoustics 2024, 6(3), 579-592; https://doi.org/10.3390/acoustics6030031 (registering DOI) - 28 Jun 2024
Viewed by 97
Abstract
The primary cause of noise from vehicular traffic while travelling at speeds over 30 km/h is tyre/road interaction. To reduce this noise source, tyre/road sound emissions research has been carried out using different approaches. Most of this research has been centred around track
[...] Read more.
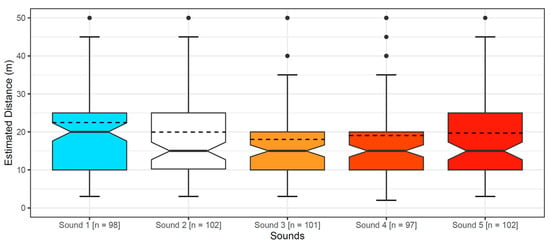
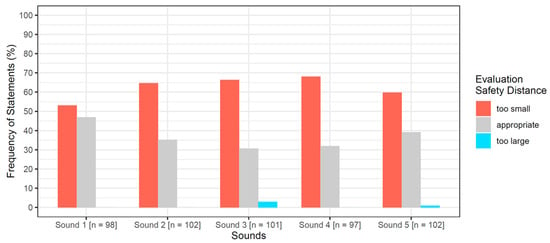
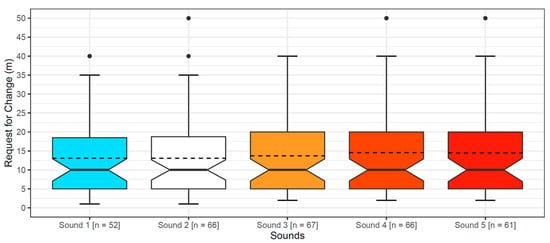
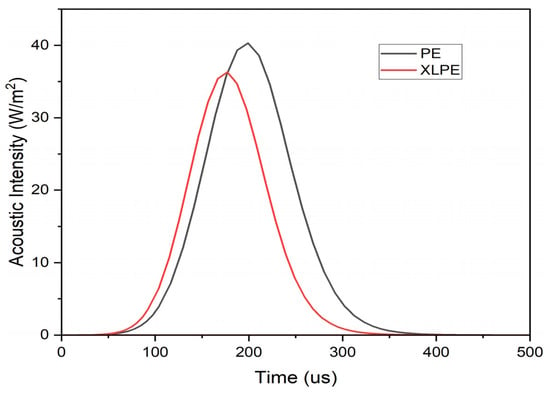
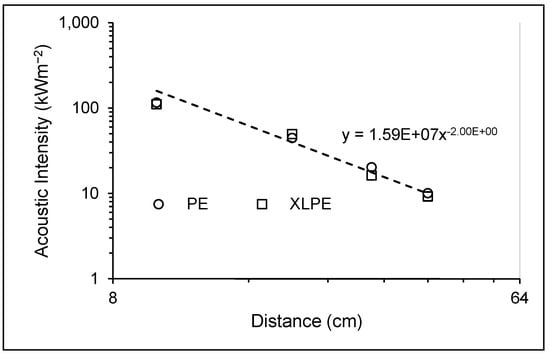
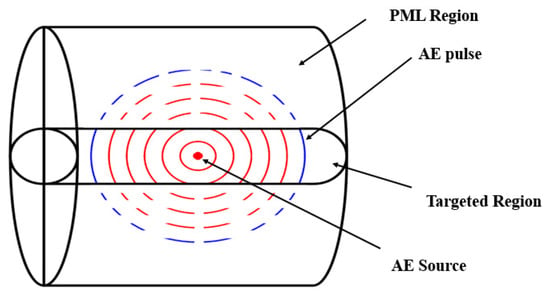
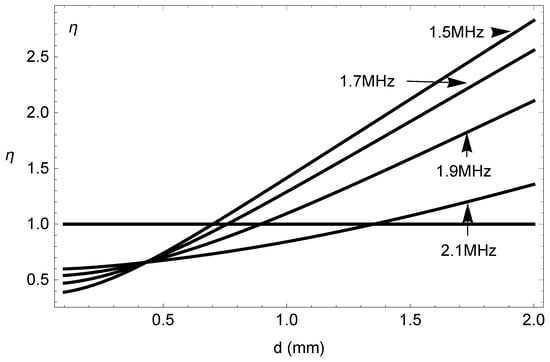
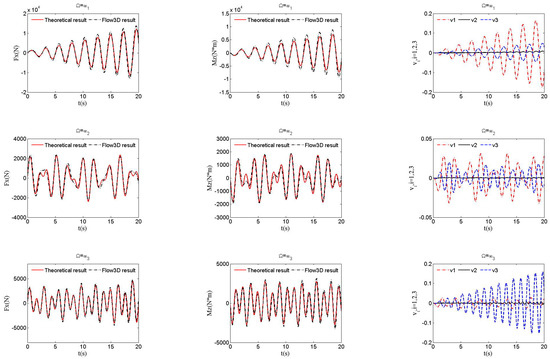
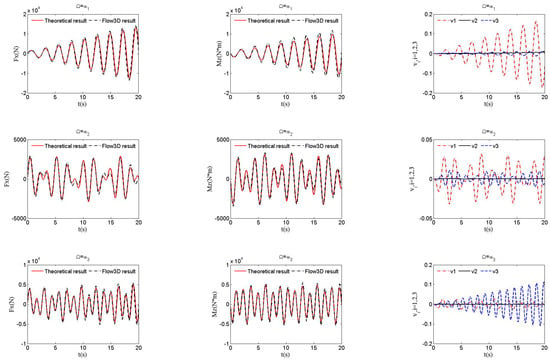
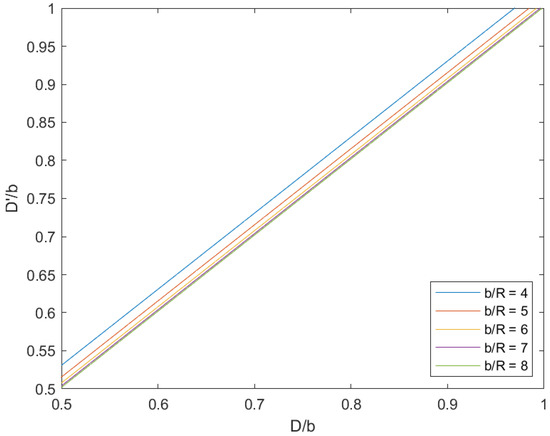
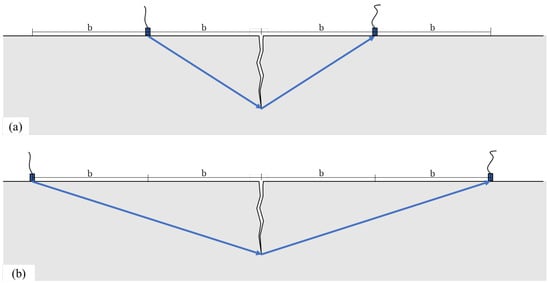
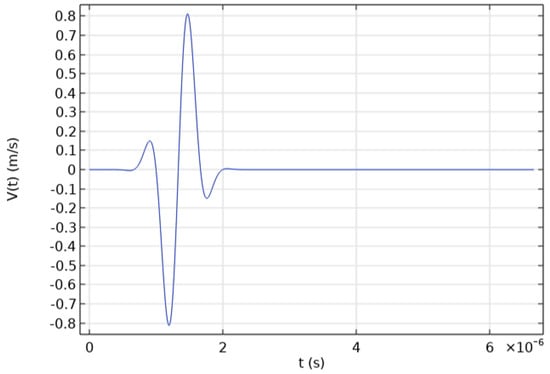
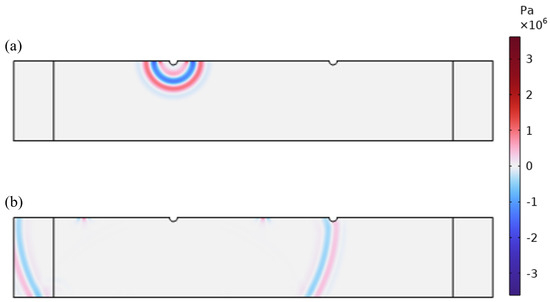
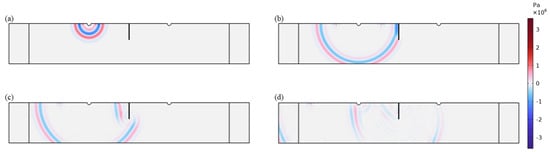
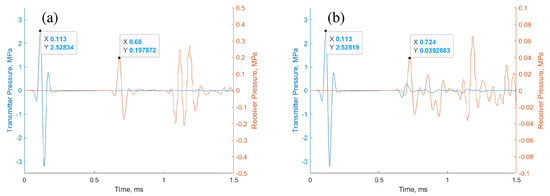
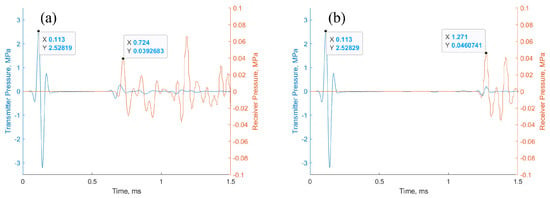
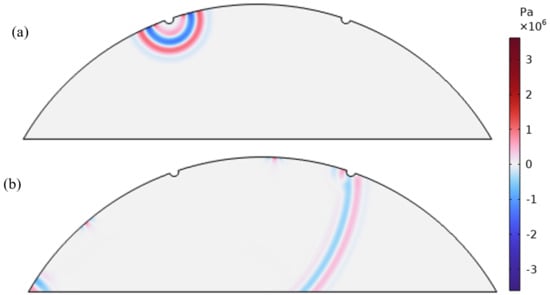
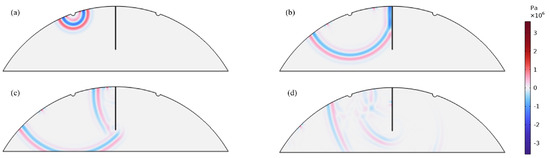
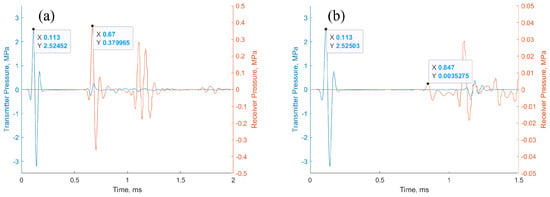
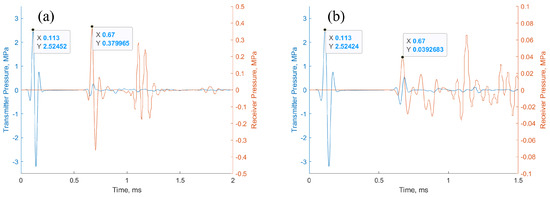
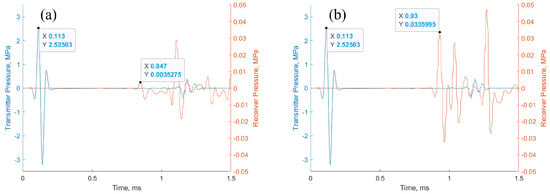
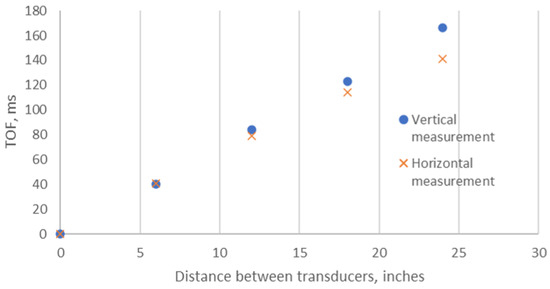
The primary cause of noise from vehicular traffic while travelling at speeds over 30 km/h is tyre/road interaction. To reduce this noise source, tyre/road sound emissions research has been carried out using different approaches. Most of this research has been centred around track tests, leading to the development of various track and road-based methods for evaluating tyre/road noise emissions. The CPX (Close-Proximity), along with the CPB (Controlled Pass-By), the CB (Coast-By) and the SPB (Statistical Pass-By), methods are the most common ones. Nevertheless, since Reg. (EC) 1222/2009 came into force, only the CB method, defined in Reg. (EC) 117/2007, can be used to obtain tyre/road noise emission type approval values in Europe. However, current track test methods have important limitations, such as the variability of the results depending on the test track or the test vehicle, the repeatability, the influence of environmental variables or, the main aspect, the limitation of the registered magnitude in these tests, which is the sound pressure level. The Alternative Drum test method (A-DR) was developed in 2015 in order to avoid these disadvantages. However, it involves a complex and time-consuming microphone array for each test. With the purpose of improving the A-DR test method, a new methodology based on drum tests, the ISO 11819-2 and the ISO 3744 standards, was developed. This paper describes the new Alternative CPX Drum test method (A-CPX-DR) and validates it by testing several tyres according to the CB, the A-DR and the A-CPX-DR test methods and comparing their results. This research has demonstrated that all three methods have equivalent sound spectra and obtain close equivalent sound pressure levels for type approval of tyres in the EU, while drum tests have shown greater accuracy. For both reasons, the new A-CPX-DR methodology could be used for tyre/road noise emission type approval in a more precise and cheaper way.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---