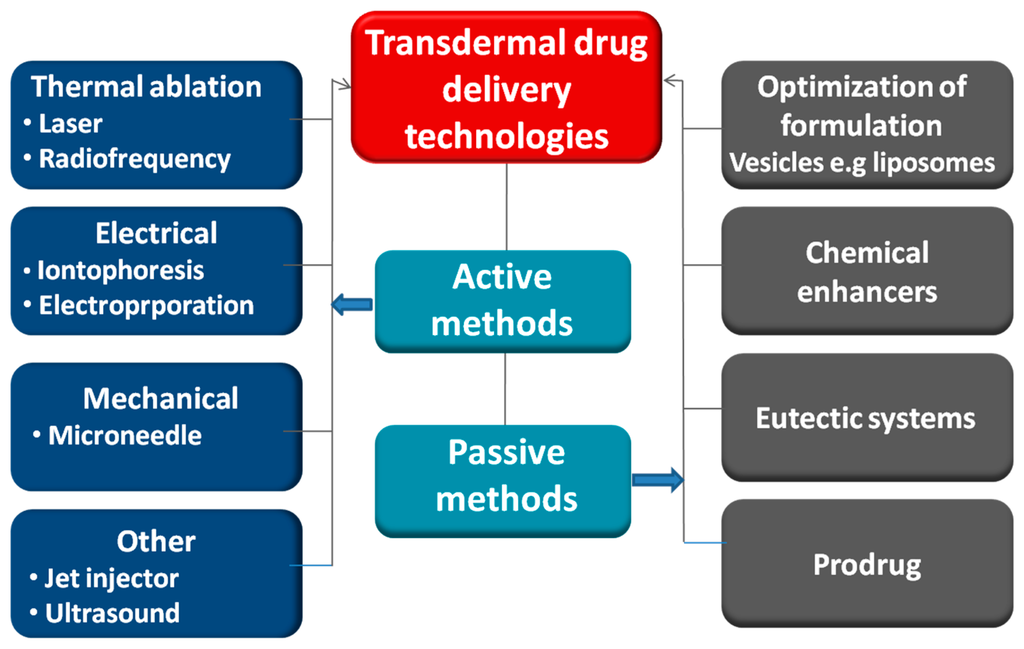
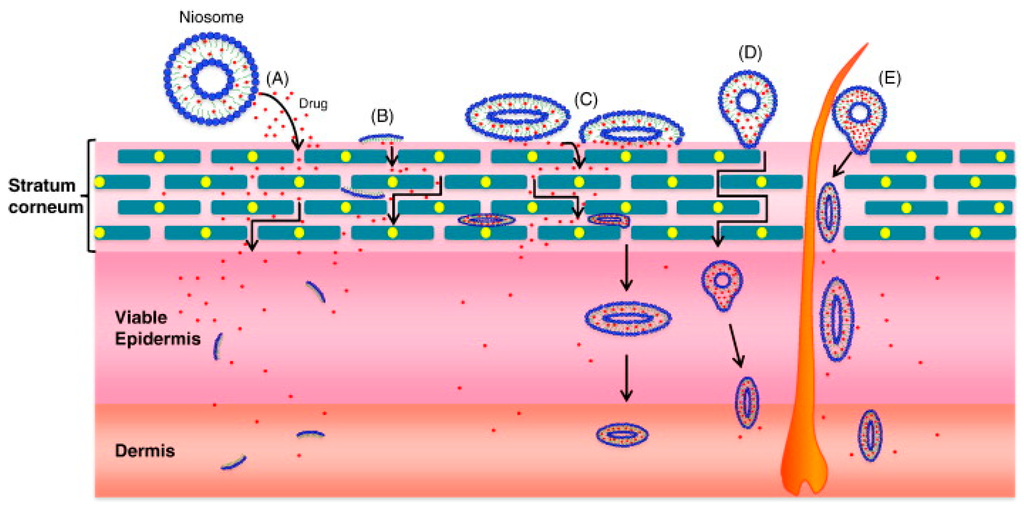
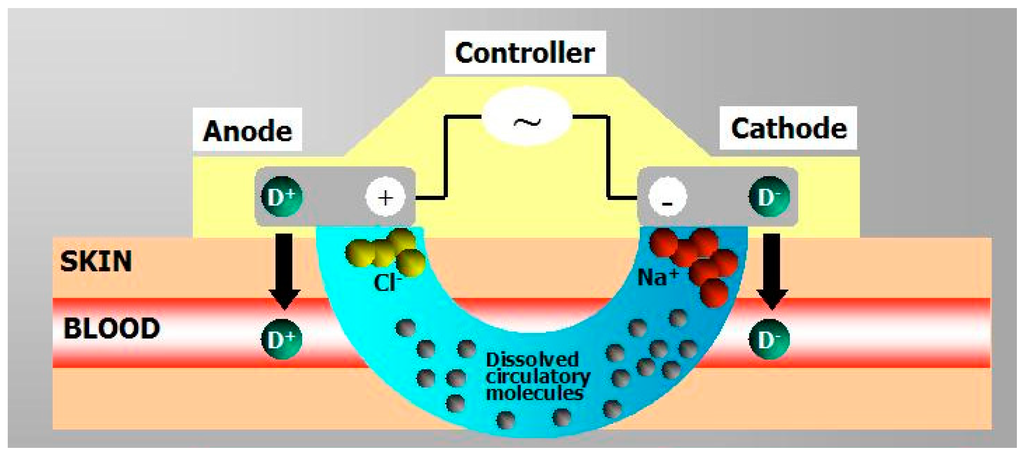
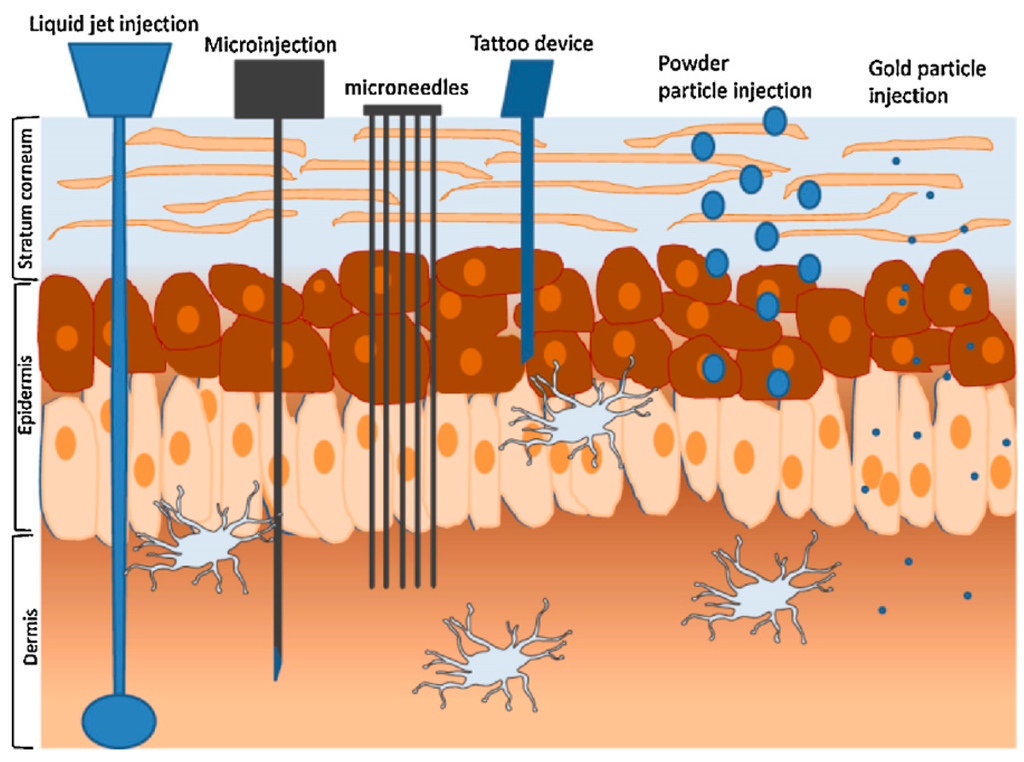
Open AccessReview
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)—Current Research on the Health-Promoting Activities: A Narrative Review
by
Paulina Mikulska, Marta Malinowska, Miłosz Ignacyk, Paweł Szustowski, Joanna Nowak, Karolina Pesta, Monika Szeląg, Damian Szklanny, Eliza Judasz, Gabriela Kaczmarek, Ovinuchi Prince Ejiohuo, Magdalena Paczkowska-Walendowska, Anna Gościniak and Judyta Cielecka-Piontek
Cited by 29 | Viewed by 44247
Abstract
In recent years, there has been a significant surge in reports on the health-promoting benefits of winter cherry
(Withania somnifera), also known as Ashwagandha. Its current research covers many aspects of human health, including neuroprotective, sedative and adaptogenic effects and effects on sleep.
[...] Read more.
In recent years, there has been a significant surge in reports on the health-promoting benefits of winter cherry
(Withania somnifera), also known as Ashwagandha. Its current research covers many aspects of human health, including neuroprotective, sedative and adaptogenic effects and effects on sleep. There are also reports of anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, cardioprotective and anti-diabetic properties. Furthermore, there are reports of reproductive outcomes and tarcicidal hormone action. This growing body of research on Ashwagandha highlights its potential as a valuable natural remedy for many health concerns. This narrative review delves into the most recent findings and provides a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of ashwagandha’s potential uses and any known safety concerns and contraindications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures