Abstract
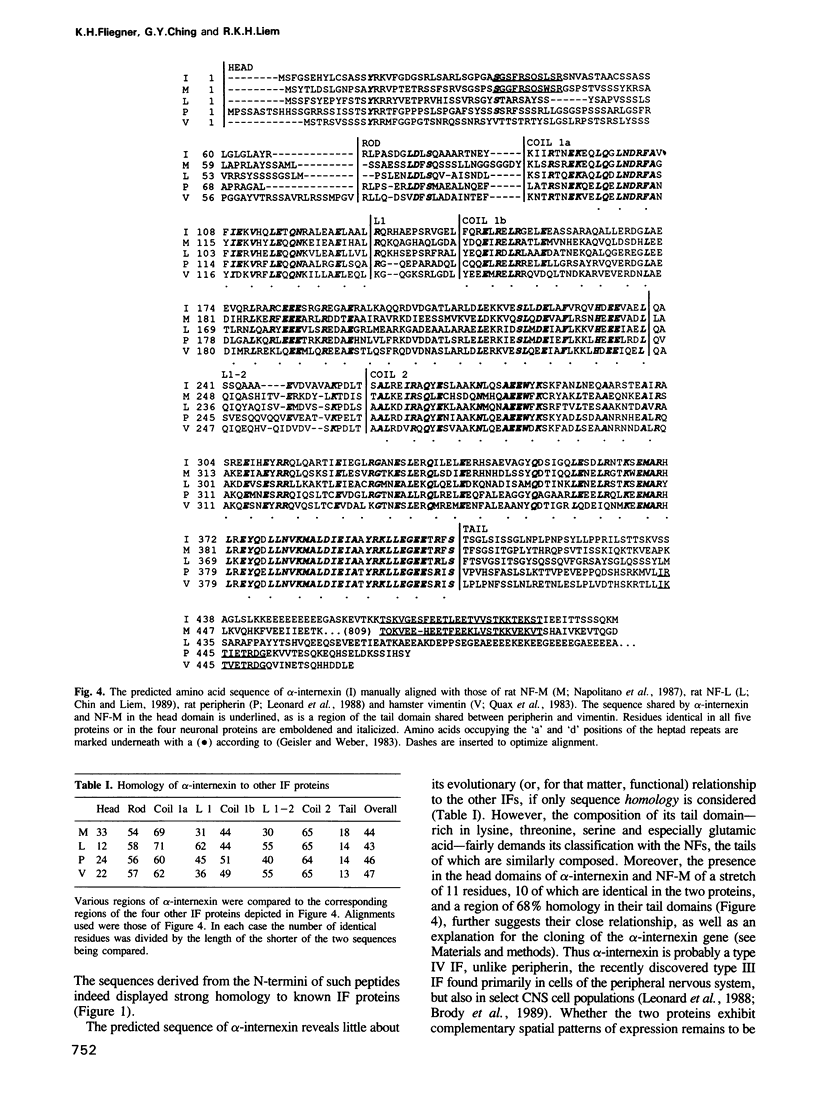
Our laboratory recently isolated and began to characterize a 66 kd rat brain cytoskeletal protein, dubbed alpha-internexin for its interactions in vitro with several other cytoskeletal proteins. Although alpha-internexin bore several of the characteristics of intermediate filament (IF) proteins, including the recognition by an antibody reactive with all IF proteins, it did not polymerize into 10 nm filaments under the conditions tested. Here we show that the predicted amino acid sequence of a cDNA encoding alpha-internexin shows the latter to be an IF protein, probably most closely related to the neurofilament proteins. Northern blotting shows that alpha-internexin expression is brain specific, and that rat brain alpha-internexin mRNA levels are maximal prior to birth and decline into adulthood, while the converse is seen for NF-L, the low molecular weight neurofilament subunit, suggesting that these two proteins play different roles in the developing brain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody B. A., Ley C. A., Parysek L. M. Selective distribution of the 57 kDa neural intermediate filament protein in the rat CNS. J Neurosci. 1989 Jul;9(7):2391–2401. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-07-02391.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin S. S., Liem R. K. Expression of rat neurofilament proteins NF-L and NF-M in transfected non-neuronal cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):475–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Barnes E. A., Das K., Haley J., Socolow P., Macaluso F. P., Fant J. Characterization of a novel 66 kd subunit of mammalian neurofilaments. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1435–1445. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. A., Liem R. K. Beta-internexin is a microtubule-associated protein identical to the 70-kDa heat-shock cognate protein and the clathrin uncoating ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15210–15215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Cleveland D. W., Griffin J. W., Landes P. W., Cowan N. J., Price D. L. Neurofilament gene expression: a major determinant of axonal caliber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3472–3476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon F., Lemonnier M., Benarous R., Huc C., Fiszman M., Gros F., Portier M. M. Multiple mRNAs encode peripherin, a neuronal intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1719–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard D. G., Gorham J. D., Cole P., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. A nerve growth factor-regulated messenger RNA encodes a new intermediate filament protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):181–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Yen S. H., Salomon G. D., Shelanski M. L. Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Przybyla A. E., Chirgwin J. M. Isolation of RNA using guanidinium salts. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:219–227. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. M. Nick translation. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:91–94. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco S., Autilio-Gambetti L., Zabel D., Gambetti P. Giant axonal neuropathy: acceleration of neurofilament transport in optic axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):920–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napolitano E. W., Chin S. S., Colman D. R., Liem R. K. Complete amino acid sequence and in vitro expression of rat NF-M, the middle molecular weight neurofilament protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2590–2599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Liem R. K. alpha-Internexin, a 66-kD intermediate filament-binding protein from mammalian central nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1316–1322. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parysek L. M., Goldman R. D. Characterization of intermediate filaments in PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):781–791. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier M. M., de Néchaud B., Gros F. Peripherin, a new member of the intermediate filament protein family. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(6):335–344. doi: 10.1159/000112360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Roop D. R. Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:593–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Ziff E. B. Structure of the gene encoding peripherin, an NGF-regulated neuronal-specific type III intermediate filament protein. Neuron. 1989 Jan;2(1):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Meinkoth J. L., Kimmel A. R. Northern and Southern blots. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:572–581. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]